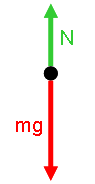| Excerpt |
|---|
|
Finding apparent weight using normal force. |
...
...
One way that we perceive weight is the normal force we experience from the ground. In physics problems, when you are asked to determine apparent weight, the quickest method is usually to compute the normal force provided by the "ground".
One way to experience a reduced apparent weight is to strap into a harness of ropes and have someone (or some weight) pull down on the other end like they do in theater or films. Another way is to jump into a swimming pool, where the water lifts up on you. Another possibility, which we explore in this problem, is to enter an environment where the "ground" is capable of moving, such as an elevator.
| Deck of Cards |
|---|
|
| Card |
|---|
| Part ASuppose a person with a weight of 686 N is in an elevator which is descending accelerating downwards at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s and speeding up at a rate of 3.0 m/s2. What is the person's apparent weight? Solution*System:* *Interactions:* | Cloak |
|---|
| External influences from the earth (gravity) and the floor of the elevator (normal force). |
*Model:* *Approach:* | | Card |
|---|
| | Diagrammatic Representations The physical picture and free body diagram for the person is: 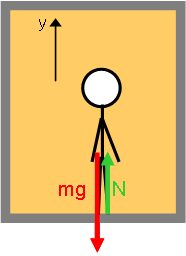 Image Added Image Added | 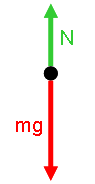 Image Added Image Added | Physical Picture | Free Body Diagram |
|---|
which leads to the form of Newton's 2nd Law for the y direction: | Latex |
|---|
\begin{large}\[ \sum F_{y} = N - mg = ma_{y} \]\end{large} |
In our coordinates, the acceleration of the person is ay = -3.0 m/s2, giving: | Latex |
|---|
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
h2. Part B
Suppose a person with a weight of 686 N is in an elevator which is ascending at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s and slowing down at a rate of 3.0 m/s{color:black}^2^{color}. What is the person's apparent weight?
h4. Solution
*System, Interactions and Model:* As in Part A.
*Approach:* As in Part A, the acceleration is negative in our coordinates. The free body diagram is also the same, and so we find the same result:
{latex}\begin{large}\[ N = ma_{y} + mg = \mbox{476 N} \]\end{large}{latex}
|
| Tip |
|---|
Is it clear why the acceleration must have a minus sign? |
| Tip |
|---|
This result for the normal force is less than the person's usual weight, in agreement with our expectation that the person should feel lighter while accelerating downward. |
|
| Card |
|---|
| Part BSuppose a person with a weight of 686 N is in an elevator which has been ascending at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s and is now slowing down at a rate of 3.0 m/s2. What is the person's apparent weight? Solution System, Interactions and Model: Approach: |
| Card |
|---|
| Part CSuppose a person with a weight of 686 N is in an elevator which is ascending, speeding up at a rate of 3.0 m/s2. What is the person's apparent weight? Solution System, Interactions and Model: Approach:| Cloak |
|---|
| | Wiki Markup |
|---|
h2. Part C
Suppose a person with a weight of 686 N is in an elevator which is ascending at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s and speeding up at a rate of 3.0 m/s{color:black}^2^{color}. What is the person's apparent weight?
h4. Solution
*System, Interactions and Model:* As in Part A.
*Approach:* The free body diagram and form of Newton's 2nd Law is the same as in Part A, except that the relative size of the forces will be different. We can see this by writing Newton's 2nd Law for the y-direction:
{latex}\begin{large}\[ N = ma_{y} + mg \]\end{large}{latex}
This time, however, the acceleration is positive (_a_~y~ = + 3.0 m/s{color:black}^2^{color}) giving:
{latex}\begin{large}\[ N = \mbox{896 N} \] \end{large}{latex}
{tip}Upward acceleration increases the perceived weight.{tip}
| |
|
|