| Panel | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||
|
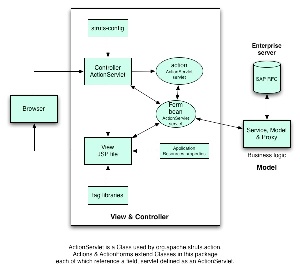
M-V-C Diagram (Model
...
-View
...
-Controller)
Model
Supported Technologies
...
The View architecture and design standards are maintained by the IS&T insideMIT Design and Development (IDD) team. IDD's documentation describes implementation rules for such View technologies as Java Server Pages (JSP), JSTL, and Apache Struts Tiles and Tag Libraries. Please refer to their documentation for specific View standards.
...
The IS&T-licensed SourceLabsSASH Stack (Spring, Axis, Struts, Hibernate) comprises the standard technologies for use in insideMIT Java applications. A SASH Stack compliant version of Apache Struts is used for Controller components.
Specifications
- It is the Action class' job to convert model data into a form that can be used by the View (if necessary).
- Every Action that handles user input has a unique Action Form. Other views have request data only . Only data that is shared across multiple pages can be stored in session scope.Action Forms should always be in Request scope (never in Session scope unless they are used across multiple pages as in a wizard(what does this mean?). Scope should be request NOT session (see struts-config).
- When an Action's algorithm is dynamic based on user input, Action-chain patterns should be used, not helper-class patterns (is this what is being done in safo?).
- Actions Actions must only perform one specific function and then either chain to another action or go to a JSP page.
- User input can be validated for correct form, but not for business rules. Business rules are maintained on back end.
- Actions Actions do not return formatted view code (XHTML).
- Collections must be documented to state what objects they contain and what properties those objects contain.
...