| Composition Setup |
|---|
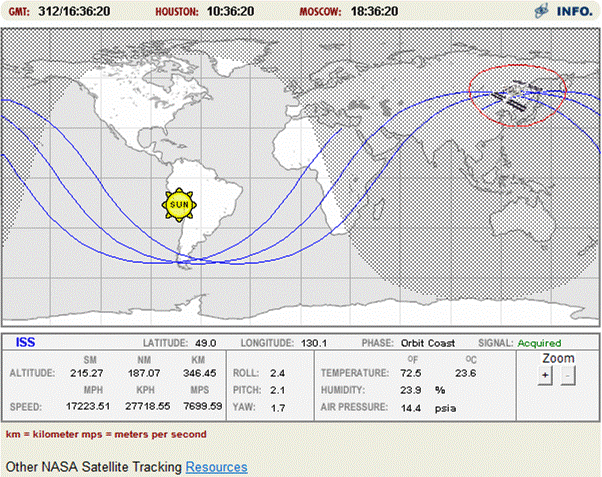
...
By navigating to the site
http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/realdata/tracking/
...
you
...
can
...
obtain
...
tracking
...
information
...
giving
...
the
...
altitude
...
and
...
speed
...
of
...
the
...
International
...
Space
...
Station
...
(ISS).
...
Suppose
...
that
...
the
...
information
...
displayed
...
on
...
the
...
site
...
was
...
as
...
shown
...
in
...
the
...
screen
...
capture
...
above.
...
By
...
making
...
the
...
assumption
...
that
...
the
...
space
...
station's
...
orbit
...
is
...
a
...
circle
...
with
...
its
...
center
...
at
...
the
...
center
...
of
...
the
...
earth,
...
| Excerpt |
|---|
find |
...
the |
...
approximate |
...
magnitude of the acceleration |
...
experienced |
...
by |
...
the |
...
space |
...
station |
...
as |
...
a |
...
result |
...
of |
...
the |
...
gravitational |
...
pull |
...
of |
...
the |
...
earth. |
Solution
| Toggle Cloak | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Cloak | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Cloak | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Toggle Cloak | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Cloak | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Cloak | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Toggle Cloak | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Cloak | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Cloak | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Toggle Cloak | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Cloak | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Based upon the assumption of uniform circular motion, the acceleration of the ISS must satisfy:
| Latex |
|---|
System: The ISS will be treated as a point particle, subject to an external influence from the earth (gravity). Model: [Uniform Circular Motion]. Approach: We know from the Law of Interaction that the acceleration experienced by the ISS must satisfy: {latex}\begin{large}\[ a = \frac{v^{2}}{r} \] \end{large}{latex} |
We
...
know
...
that
...
v
...
=
...
7699.59
...
m/s,
...
but
...
r
...
requires
...
some
...
thought.
...
The
...
altitude
...
of
...
346450
...
m
...
is
...
not
...
the
...
full
...
radius
...
of
...
the
...
orbit,
...
it
...
is
...
only
...
the
...
height
...
of
...
the
...
ISS
...
above
...
the
...
surface
...
of
...
the
...
earth.
...
To
...
find
...
the
...
full
...
orbital
...
radius,
...
we
...
must
...
add
...
on
...
the
...
earth's
...
radius.
...
The
...
earth's
...
radius
...
can
...
be
...
found
...
on
...
the
...
web
...
or
...
in
...
a
...
number
...
of
...
books
...
to
...
be
...
R
...
e =
...
6,380,000
...
m.
...
Thus,
...
the
...
orbital
...
radius
...
is
...
r
...
=
...
6,730,000
...
m.
...
With
...
this
...
determined,
...
we
...
find:
| Latex |
|---|
}\begin{large} \[ a = \mbox{8.81 m/s}^{2} \] \end{large}{latex} {note} |
| Note |
|---|
Earth's gravity is *not *insignificant at level of the ISS's orbit. If it was, the ISS would just fly off into space! {note} |
| Cloak | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||