- Calendar View:
Manasi Vartak, Tristan Naumann, Chidube Ezeozue
Demo: http://youtu.be/xuxCxUd0bqM
We used a SmartBoard for our implementation instead of a web or mobile interface because user studies indicated that users would not go out of their way to get information about events through a website or mobile app. In fact, the events.mit.edu website which is a central repository for events, is hardly used by students. We envision SmartBoards (or a similar devices) being placed at the current locations of poster boards in Stata. We also chose to allow adding of posters through the smart board as opposed to having a separate web interface for simplicity and uniformity of the interface.
In our final design, we implemented two views to organize posters on the PosterBoard, one view to add a poster, and a detailed view to interact with the selected poster. We decided against the "Random view" for viewing posters because it did not aid users in finding relevant information.




In the course of our design, we made changes driven by comments in our paper prototype and heuristic evaluation. Our user testing also threw some insight on possible future improvements.
Paper Prototype
Heuristic evaluation
We implemented the project using a SmartBoard PN342C 4-point optical touchscreen that plugged into any computer's serial/USB ports to register touch input and accepted VGA/DVI for display. To minimize dependency on the SmartBoard, we implemented the project as a website and projected it using the SmartBoard. This allows the project to be viewable from anywhere, even though we optimized the experience for the SmartBoard.
The backend for content was implemented primarily in Python using the Django web application framework and SQLite database. Because a browser implementation is sandboxed with respect to system hardware, we also wrote a standalone server in Python to relay inputs from the RFID reader to the frontend. The frontend was implemented using HTML, CSS and Javascript with a heavy reliance on the JQuery and JQuery UI libraries as well as a few other libraries. These libraries were utilized in the following ways:
Likewise, a more detailed list for the components necessary for deployment of the project can be found in the README file on github: https://github.com/tnaumann/PosterBoard/blob/master/README. Further, in order to implement a backend sufficient for the purposes of the demo, we made the following considerations:
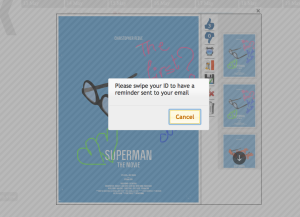
One of the challenges we faced after paper prototyping was the realization that in our original concept's on-screen keyboard was simply not comfortable or efficient. While such keyboads may be efficient for mobile devices and tablet PCs, we were forced to consider alternative solutions. Ultimately, we decided to use an RFID reader to grab information from the user which would allow us to populate the email field when adding a poster as well as confirm a user's identity when sending reminders and attempting to delete a poster. Of course, this solution required not only the acquisition of a suitable RFID reader but also a mechanism for the RFID reader to supply information to the application which was running in a browser and consequently unable to receive information from system-specific input devices. The first attempted solution to this problem leveraged javascript in order to enable it to talk to the Django server in order to communicate indirectly to the application through the backend, however this failed. A subsequent attempt was able to run at the Django server, but the single-threadedness of the Django development server implementation meant that waiting on RFID events would block content service and vice versa. Clearly not suitable. Finally, the implementation of a websocket server built on the RFID reader code was developed in order to relay information from the RFID reader directly to the frontend independent of Django. The complexity of this interaction meant that the working implementation was only available a week before GR5, thus limiting our ability to take further advantage of its capabilities.
Likewise, our dependence on the SmartBoard hardware in order to provide touch input lead to over 30 hours of technical phone support from SMART, and several additional components either purchased from SMART or mailed to us from support technicians who were unable to diagnose the problems further without exhausting the slew of troubleshooting techniques which require their hardware. The final working connection with the board was facilitated by a proprietary serial-to-USB cable which SMART does not sell via their online store and was only obtained after exhausting all other connection capabilities available on their website. Consequently, the working touch solution was only available days before the completion of GR5.
A side-effect of this problem was the need to completely resize our interface prior to demo since we had all been developing on machines with significantly higher resolution or different aspect ratios than the SmartBoard. It also meant that we could not customize our application to the specific touch facilities of the hardware. Specifically, out interface assumes that the touch hardware will relay touch information reliably while in reality the SmartBoard was neither as responsive nor as accurate as we would have hoped. Had we know this, we could have provided larger click regions for visible buttons, altered our spacing, and created more feedback so that the perceptual fusion was a bit stronger. Further, the use of optical touch meant that we were forced to rely on only a single input point which precluded our former use cases for allowing multiple users to interact with the board as well as those which considered gestures.
The ideal user test would have been conducted by moving the board to a part of the building with high human traffic and the test conducted with people who were attracted to the board in the first place. We however did not have that luxury because the board was fixed in place at the group space of a research group. We however managed to conduct a test that was very revealing and helpful.
Choice of users
We were looking for users that were representative a the bulk of the population in MIT: students and we had 3 users: 1 female postdoc who recently completed her PhD in New York, 1 male PhD student working in CSAIL and **Tristan fill in here**. In order not to focus solely on students, we performed a demo of the project for a professor as well and got some helpful comments from him.
User preparation
We utilized our briefings and tasks (outlined below) from the paper prototyping exercise with one slight modification.
Briefing
PosterBoard is a project that aims to increase visibility of event posters by encouraging interaction with the posters.
What you are looking at is an electronic poster board that will be installed up in a public place like the ground floor of the Stata center.
Scenario Tasks
Task 1: You have come across this poster board in Stata Center. Describe 5 things you can do with it. Interact with it for two minutes. (We utilized this open ended task to get a sense for which features of the poster board were discoverable as well as those that might be expected).
Task 2: You have a USB drive in your possession. Add a poster from the USB onto the poster board.
Task 3: Find a poster you like, add it to your calendar and scribble on it.
Observations
User Testing. If we were going to make further changes, we would make the following changes based on user testing feedback.
Risk assessment: We under-estimated the risk involved due to hardware. Specifically, the project turned out to be much more hardware focused than we expected since our application was heavily dependent and limited by the SmartBoard and RFID equipment. As mentioned above, the SmartBoard was not fully functional until the last week of classes. As a result, we could not optimize out functionality for the SmartBoard resolution and size. Further, since we wanted to completely remove the need for typing, it was essential that we have an alternate mechanism of getting user information. We used an RFID reader for this purpose. However, this again introduced a hardware dependency and we had to focus on getting the RFID reader to work with our server. Since we got a working RFID prototype ready in the last few weeks, extensions to the functionality using this capability were severely limited. In particular, we wanted to implement personalization of the PosterBoard based on the time a user last visited the board and preferences for events. However, we cut this feature due to time constraints. This feature would also have introduced a new "personalized" mode in the system that we felt would confuse the user and could open up safety issues like another user using the previous user's information to post posters or information. It would also have been beneficial to have backup plans in case the hardware didn't go through. We had partially mitigated this risk by implementing the project as a webpage but we could have explored other alternatives.
User testing: Testing the prototypes without the SmartBoard made it difficult for us to judge how interaction with the board will differ form interaction on a computer. The environment in which we tested the prototype was also different from the actual environment. Since we briefed users about the project, its purpose and high-level functionality. However, this did not allow us to test the discoverability of the PosterBoard purpose and functionality. Moreover, we were unable to observe how users would interact with the touch interface since heuristic evaluation was done using a mouse and keyboard.
Prototypes: The set of features we prototyped was good. It would have been beneficial to more fully prototype the functionality. Since the backend was missing, we were unable to provide system status updates and hence this part was not tested. We could also have put the paper prototype on a vertical board and observed peoples' interaction. It would also have helped to prototype at scale. Using a UI designed for a computer screen on the SmartBoard did not give good results.
- evaluating results of observation: each user test had new people, so each time we found new problems but no feedback on whether the old problems had been fixed
- implementation details that caused problems: saving scribbles was really time consuming which caused a bug where detailed posters did not appear properly
- focus less on the functionality and more on the interface
Safety: One thing we think is very important in a project like this is safety. The user testing revealed that with a touch screen board hanging in a public place (as opposed to the safety and comfort of a room or office) was prone to accidental taps and brushes and the project has to be able to provide a user interface that takes care of that aspect to create a less frustrating experience.