Useful Information
See more information about the problems in Class Notes Lecture 5
Problem 0 - Imaging on Cylinder
Flow is along y-axis
What are the acquired image and the velocity, position, diffusion signatures?
Problem 1 - Periodic
- Show that for average over φ, we get pure absorptive line-shape, and for a particular isochromat, average over φ in general has dispersive line-shape (Show the response in cylindrical coordinate)
- Normal shim: x,y (first order spherical harmonic). Show that if there are terms x^2-y^2, xy, then the sideband will show up at twice Ω
- Calculate the FID and the spectrum for rotary vs non-rotary, then plot them on top of each other
Problem 2 - Chemical Shift
- Show that chemical shift tensor
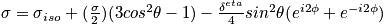
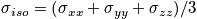
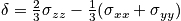
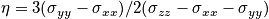
- Show that under random rapid motion spins
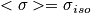
It average out any non-isometric parts, so we have a homogeneous sample. So the result does not depend on the orientation of the sample.
When η = 0 -> < 3cos(θ)^2 -1 > = 0, average over sphere
- η = 0 ; calculate the line-shape for static powder (constant orientation with magnetic field), η ≠ 0 ; reduce to a summation over η. [Hint: can be written in elliptical integral, check out appendix I ]
- Find σ(θ,φ), powder distribution of the sample (when spinning at the magic angle ?)
Problem 3 - Decoherence
- What is the contribution of the chemical shift anisotropy to T2?
Problem 4 - Carl-Purcell Sequence
- Look at diffusive attenuation of water rotating in magnetic field gradient. Show that the faster you rotate it, the effective T2 is approaching T2.
Problem 5 - Chemical Exchange
- Show the plot of the chemical exchange (when τ|ΔωA-ΔωB| approaching 1, the 2 peaks merge at the center) [Hint: check out appendix F]
Problem 6 - Slow Exchange
- Show that by collect this terms in slow exchange
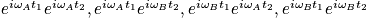
then do phase cycle and collect data set
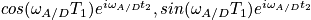
Then we get pure absorptive line-shape