The change in angular position with time, the angular analogue of linear velocity. It is a vector, having both magnitude and direction. In introductory mechanics we will almost always deal with cases of angular velocity about a single axis of rotation, so that the angular velocity is confined to one dimension.
Mathematical Definition
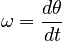
Because we will always deal with one-dimensional angular velocity (more specifically, the angular velocity about one chosen axis of rotation in any given problem), we have dropped the vector arrows from the definition.