ConcavityandAcceleration"> Concavity and Acceleration
Deceleration"> Deceleration
AccelerationversusDeceleration"> Acceleration versus Deceleration
In everyday speech, we distinguish between "accelerating" and "decelerating". In physics, both situations are referred to as acceleration (which can be confusing). It is possible to give an exact definition of deceleration, however. Deceleration occurs when the velocity and the acceleration vectors have opposite directions. "Acceleration" in the everyday sense (speeding up) occurs when the acceleration vector and the velocity vector have the same direction. The two cases can be distinguished graphically.
GraphsShowing"Acceleration""> Graphs Showing "Acceleration"
null |
null |
positive acceleration |
negative acceleration |
|---|
Both the graphs that show "acceleration" have slopes that are steepening with time. The only difference is that one of the graphs has a steepening positive slope and the other has a steepening _negative slope.
GraphsShowingDeceleration"> Graphs Showing Deceleration
null |
null |
negative acceleration |
positive acceleration |
|---|
Both graphs showing "deceleration" have slopes that are approaching zero as time evolves. (Again, one has a negative slope and one has a positive slope.)
It is a very common misconception that a negative acceleration always slows down the object it acts upon. This is not true. It is important to note that a graph which has a negative slope approaching zero (slowing down) implies a positive acceleration, and a graph which has a negative slope that is steepening (speeding up) implies a negative acceleration. It may help you to remember that the concavity of the graph specifies the direction of the acceleration.
Check Your Understanding"> Check Your Understanding
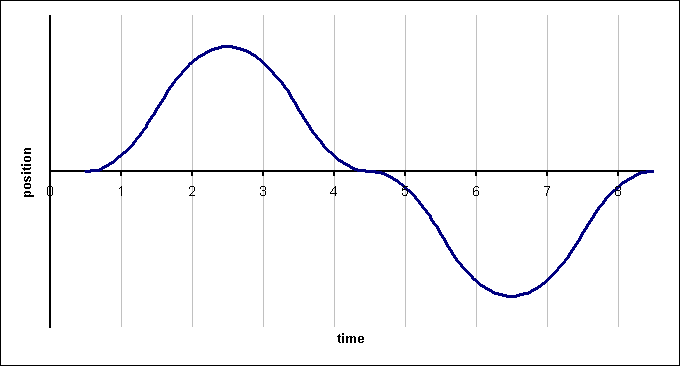
By looking at the position versus time graph shown above, determine the following at each of the eight numbered instants of time:
A.) Is the object's position positive or negative?
B.) Is the object's velocity positive or negative?
C.) Is the object's acceleration positive or negative?
D.) Is the object speeding up (accelerating) or slowing down (decelerating)?
Solution
System, Interactions and Model: This exercise is a review of the definitions of position, velocity and acceleration. These concepts are used in several of the models in the hierarchy.
Answers: