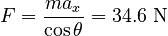Part A
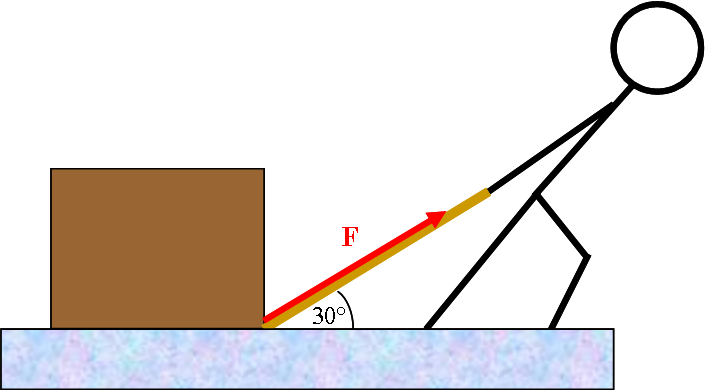
A person pushes a box of mass 15 kg along a smooth floor by applying a force F at an angle of 30° below the horizontal. The box accelerates horizontally at a rate of 2.0 m/s2. What is the magnitude of F?
Solution
System:
Box as point particle.
Interactions:
External influences from the person (applied force) the earth (gravity) and the floor (normal force).
Model:
Approach:
Diagrammatic Representation
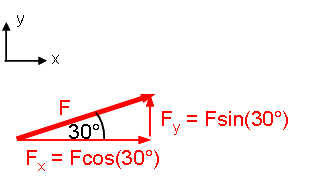
Before writing Newton's 2nd Law for the x direction, we choose coordinates and break the applied force F into x- and y-components:
Mathematical Representation
Using the free body diagram, we can write the relevant x-component of Newton's 2nd Law:
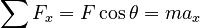
Solving for F:
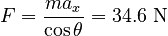
Part B
A person pulls a box of mass 15 kg along a smooth floor by applying a force F at an angle of 30° above the horizontal.. The box accelerates horizontally at a rate of 2.0 m/s2. What is the magnitude of F?
Solution
System:
Box as point particle.
Interactions:
External influences from the person (applied force) the earth (gravity) and the floor (normal force).
Model:
Approach:
Diagrammatic Representation
Before writing Newton's 2nd Law for the x direction, we choose coordinates and break the applied force F into x- and y-components:
Mathematical Representation
The free body diagram implies:
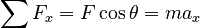
Solving for F: